Mediterranean Food: A Flavorful Trip With Custom and Taste
Mediterranean cuisine serves as an exceptional junction of practice and preference, attracting from a varied variety of societies that extend continents. The extensive tastes and health benefits associated with the Mediterranean diet have gathered international affection, yet beneath its surface area exists an intricate story of historical impacts and regional specialties that require further exploration.
Beginnings of Mediterranean Cuisine
The origins of Mediterranean cuisine are deeply rooted in a rich tapestry of background, location, and social exchange. This cooking practice arises from an area defined by its diverse landscapes, consisting of coasts, hills, and abundant levels, which have influenced its farming techniques and food production. The Mediterranean Basin, encompassing nations such as Italy, Greece, Spain, and Turkey, has been a crossroads of worlds for millennia, where trade routes helped with the exchange of ingredients, techniques, and cooking philosophies.
Ancient cultures, consisting of the Greeks and Romans, dramatically designed Mediterranean foodways, highlighting the importance of fresh, seasonal produce and communal eating. The spread of agriculture, particularly the farming of olives, grains, and grapes, laid the foundation for recipes that remain staples today. Furthermore, the impact of different conquerors and traders, such as the Moors and Ottomans, introduced new flavors and cooking designs, further enriching the food.
Today, Mediterranean food is celebrated not just for its flavor and diversity yet also for its focus on healthy eating, personifying a balanced technique to nourishment that remains to appeal to worldwide tastes. This historic interplay of ingredients and cultures creates the essence of what we currently identify as Mediterranean food.
Key Active Ingredients and Flavors
Mediterranean cuisine is characterized by a lively array of essential components and tastes that reflect the region's agricultural bounty and social heritage. Central to this cooking tradition are fresh vegetables, fruits, and herbs, which give essential nutrients and dynamic tastes. mediterranean restaurant las vegas. Staples such as tomatoes, eggplants, olives, and bell peppers are frequently featured, showcasing the area's varied environment and dirt
Olive oil, frequently considered as the foundation of Mediterranean food preparation, conveys richness and depth to dishes. It is matched by a range of herbs and flavors, including oregano, basil, and garlic, which elevate the flavors of meats, fish and shellfish, and grains. Grains, especially wheat and rice, act as essential elements, with meals like couscous and pasta being staples across the region.
Additionally, legumes such as chickpeas and lentils not just provide protein but additionally contribute to the cuisine's robustness. Jointly, these components create an unified equilibrium that specifies Mediterranean cuisine.
Regional Variations and Specializeds
Diverse local variants and specialties identify Mediterranean cuisine, reflecting the one-of-a-kind social impacts, geography, and background of each area. In the seaside regions of Italy, for instance, fish and shellfish rules supreme, with dishes like Sicilian caponata showcasing a mix of eggplant, olives, and capers. Greece is renowned for its use of feta cheese, olives, and fresh natural herbs, evident in traditional preparations such as moussaka and spanakopita.
The Levantine nations, including Lebanon and Syria, stress using grains and spices, with specializeds like tabbouleh and kibbeh taking center stage. North Africa, especially Morocco, sticks out for its aromatic tagines and couscous, usually enriched with dried fruits and an abundant selection of flavors.
On the other hand, the Iberian Peninsula highlights making use of healed meats and bold tastes, with Spanish paella and Portuguese bacalhau exhibiting the area's culinary diversity.
Each Mediterranean region not only commemorates its local components yet additionally reflects the historical trade paths and cultural exchanges that have shaped its food society, developing a vibrant tapestry of flavors that captivates the taste.
Food Preparation Techniques and Styles
Cooking methods and styles in Mediterranean cuisine are as varied as the regions themselves, usually reflecting neighborhood practices and available ingredients. The heart of Mediterranean cooking depends on its simpleness, where fresh produce, natural herbs, and olive oil take spotlight. Strategies such as grilling, toasting, and sautéing are generally used, permitting the all-natural flavors of the active ingredients to radiate.
Cooking, widespread in coastal locations, instills fish and shellfish and meats with a great smoky richness, while roasting, specifically in the Middle East, enhances the sweet taste of origin vegetables and meats. Sautéing, often utilized in Spanish and italian meals, supplies a quick approach to bring out the splendor of garlic and onions, working as a structure for numerous sauces.
Stewing is an additional crucial method, particularly in North African cuisines, where tagines simmer fragrant spices and tender meats gradually, blending flavors with time - mediterranean restaurant las vegas. Baking, especially in the context of bread and pastries, holds a substantial location in Mediterranean culture, with each area flaunting its very own specialties. Overall, these varied cooking approaches not only commemorate the ingredients yet likewise reflect the ingrained culinary heritage of the Mediterranean, making each meal a testimony to its rich background
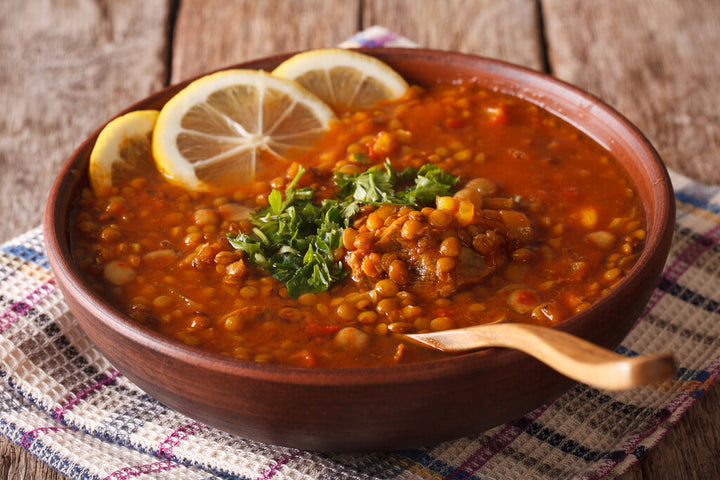

Wellness Advantages of Mediterranean Diet
Frequently recognized for its numerous wellness advantages, the Mediterranean diet plan stresses the usage of entire, minimally processed foods that promote general wellness. This dietary pattern is abundant in fruits, vegetables, entire grains, vegetables, nuts, and healthy fats, especially olive oil, while encouraging modest intake of fish and fowl and limiting red meat and sweets.
Research study regularly links the Mediterranean diet regimen to a range of health benefits. Notably, it has actually been related to a decreased threat of heart diseases, mainly due to its focus on heart-healthy fats and anti-oxidants. The diet is additionally my latest blog post thought to enhance cognitive feature and may reduce the threat of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's.
In Addition, the Mediterranean diet plan sustains weight management with its emphasis on nutrient-dense foods that promote satiation. The high fiber material from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains help food digestion and assists keep healthy blood glucose levels.
Along with physical health and wellness, the Mediterranean diet plan promotes social wellness, as it motivates public meals and shared cooking experiences. Overall, adopting this diet regimen is not just go now a path to enhanced health and wellness but likewise a party of tastes, culture, and neighborhood.

Final Thought
Finally, Mediterranean cuisine acts as a rich tapestry of practice and taste, showcasing varied regional flavors and ingredients. The emphasis on fresh produce, olive oil, and fragrant herbs not just enhances cooking experiences but likewise advertises many health benefits. By embracing classic food preparation methods and cultivating communal dining, this cooking heritage continues to motivate and connect people throughout societies, strengthening its status as a valued and influential part of worldwide gastronomy.
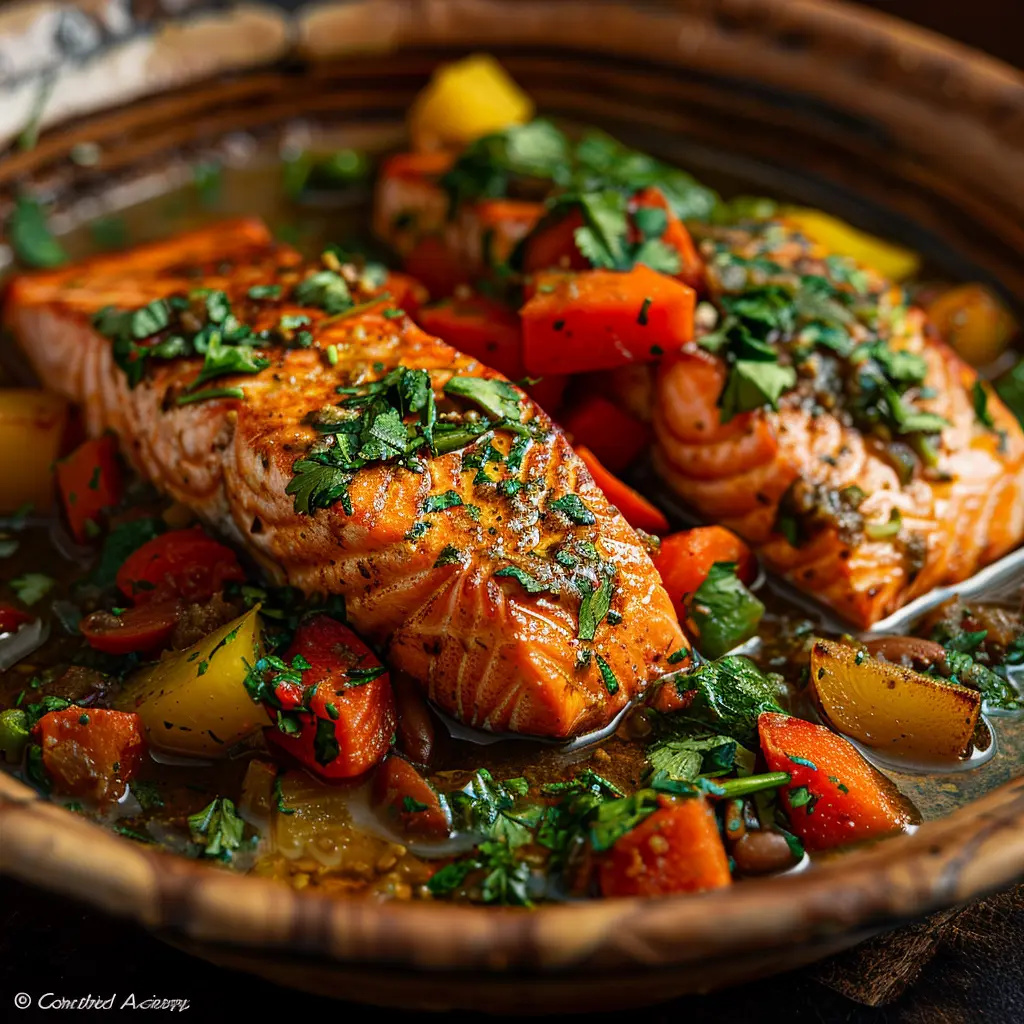
Cooking strategies and styles in Mediterranean food are as differed as the regions themselves, often showing neighborhood traditions and readily available components.In conclusion, Mediterranean cuisine offers as an abundant tapestry of custom and taste, this link showcasing varied local tastes and active ingredients.